You have received this leaflet because you have developed a cyst abscess of the Bartholin’s gland.
The information below will help explain this condition and the treatment options available.
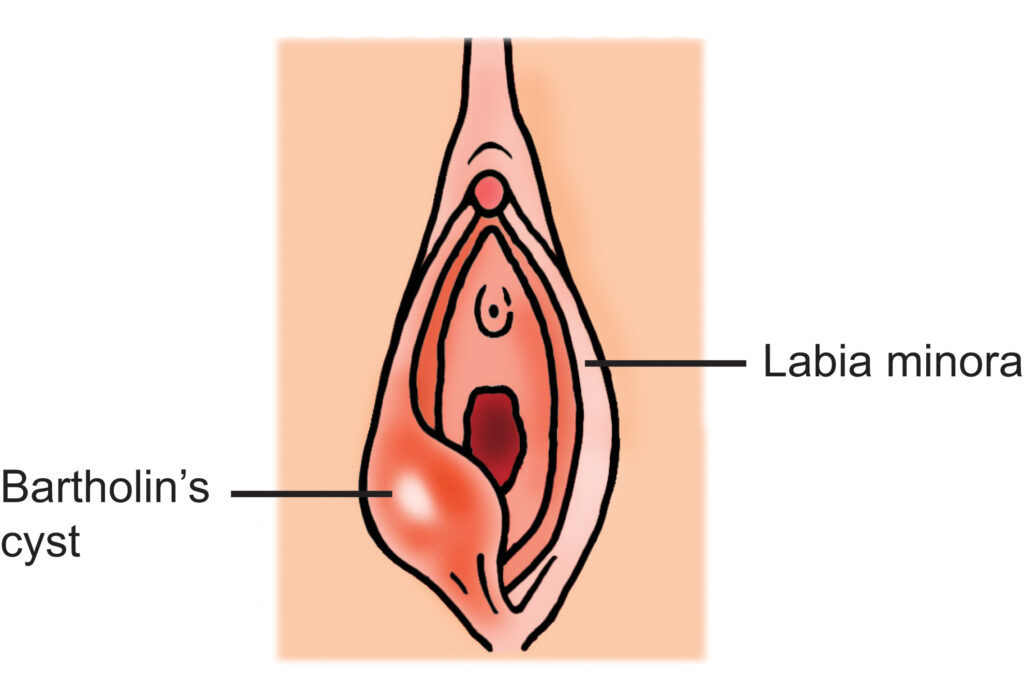
What is a Bartholin’s gland?
The Bartholin’s glands are sacs that produce fluid and are located on both sides of the vaginal opening. Normally they are not noticeable. Their job is to secrete a fluid, through a duct, into the vagina to keep it moist.
What is a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess?
A Bartholin’s cyst or abscess can develop in 2% (2 in 100) of the population.
A Bartholin’s cyst (fluid filled sac), which is normally not painful, forms when the duct leading from the gland to the vagina becomes blocked. It is unclear why this happens and there is little that you can do to prevent it.
A Bartholin’s abscess (infected pus-filled sac), which is normally very painful, develops when a Bartholin’s gland becomes infected.
What are the signs and symptoms of a Bartholin’s cyst and abscess?
A cyst or abscess can vary in size from the size of a small pea up to the size of a tennis ball. A Bartholin cyst can sometimes go unnoticed or have few symptoms.
Symptoms of a Bartholin’s abscess may include:
- A tender lump on one side of the vagina where the ducts are situated.
- Surrounding area that looks red, swollen and hot to touch.
- Discomfort and/or pain that is worse when pressure is applied e.g., when sitting or walking.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Pus oozing from the abscess (sometimes foul smelling).
- Discomfort when passing urine (stinging sensation).
What are the treatment options for the cyst or abscess?
Your doctor will discuss the most appropriate treatment options with you and explain the risks and benefits to you.
‘Watch and wait’ or expectant treatment
If you have a small cyst that is causing little or no symptoms then it may be best to leave it alone. The same is true if you have an abscess that has already started to discharge.
Usually these will resolve with time. Take pain relief and soak the area in warm water up to three times a day for 20 minutes at a time to help relieve symptoms and to encourage the cyst to burst or the abscess to discharge further.
However, if the cyst becomes painful or the abscess stops discharging and grows bigger you may need further treatment.
Antibiotic treatment
If you have a small abscess (smaller than 3 cm) and the doctor feels that you would not benefit from surgery, you may be offered a course of antibiotics. This has a good chance of curing small abscesses.
If you have had expectant or medical management of your Bartholin’s cyst/ abscess you may be asked to come back to the acute gynaecology unit within a week to see if your symptoms are improving. Your doctor will discuss this with you.
Surgical treatment
There are three surgical options that you may be offered. These are Balloon Catheter insertion, Marsupialisation or Surgical excision.
Balloon Catheter insertion under local anaesthetic
This is the preferred surgical way to treat Bartholin’s cyst or abscess. This is a procedure that is performed under local anaesthetic. It takes 5-10 minutes to perform.
A local anaesthetic is given. Then an incision (cut) is made into the cyst or abscess to allow the fluid or pus to drain out. A swab is taken to test for the bacteria which caused the infection. Occasionally, a small sample of tissue is taken from the cyst wall. Then a Balloon catheter which is a small balloon catheter is put into the opening. It is left in place for up to 4 weeks to allow fluid to come out. This method reduces the risk of a recurrence. The catheter may fall out before the four weeks are over. This is not usually a problem and you should still heal successfully. However, if it falls out within 5 days of having it put in we would recommend that you get seen by a doctor and you may need another one inserted.
What to expect before the procedure
If you have been diagnosed with a Bartholin’s abscess or cyst, you can normally have this procedure performed during the same visit.
You may be advised to take pain relief before and after the procedure.
When is it possible to go home?
You should be able to go home soon after the procedure (within 1 hour).
Please make sure you take pain medication (such as paracetamol and ibuprofen) when you get home if you feel discomfort.
What to do when you go home
If you have had a Balloon catheter inserted under local anaesthetic you should be able to return back to normal daily activities (including exercise and sex) within 3 days. You will be offered an appointment to be seen back in the acute gynaecology clinic for removal of the catheter and a review of your symptoms in four weeks’ time.
Marsupialisation
This is a procedure that is performed either under local (where you are awake but the area is numbed) or general (when you are asleep) anaesthetic. It takes 10 to 15 minutes to perform.
An incision (cut) is made into the cyst or abscess to allow the fluid or pus to drain out. This leaves a small opening or pouch that is kept open with dissolvable stitches.
The operating doctor may insert a small piece of gauze into the pouch to aid the remaining pus/fluid to drain and to reduce the risk of another cyst reforming.
What to expect before the procedure
You are usually allowed home to come back for surgery within the next two days.
Please be aware that if, due to other very unwell patients requiring surgery, your operation cannot be done before midnight on the day of your admission we will cancel your operation until the next day. For patient safety reasons we do not operate during the night unless your condition is life threatening.
When is it possible to go home?
In most cases you should be able to go home within six hours of having your operation. The nurse will check that you are able to walk around and pass urine and will also check your wound before you go home.
Important
If you have a gauze wick in the wound after your operation this must be removed prior to you going home.
Please make sure you take pain medication (such as paracetamol or ibuprofen) when you get home if you feel discomfort.
What to do when you go home
Rest for two or three days after leaving the hospital.
- Take daily baths or showers. Avoid scrubbing or rubbing area vigorously for at least two weeks. Avoid bubble bath, oils and talcum in that area while wound is healing.
- Avoid sex until there is no discharge and you are pain free.
- Take pain medication if you need them.
- Avoid tight fitting clothes e.g. slim fit jeans or underwear until you are pain free.
If there is evidence of infection in the skin surrounding the Bartholin’s abscess (cellulitis) you may be prescribed a course of antibiotics.
Please note
You do not usually need to be seen again once you have been discharged home.
Comparison of balloon catheter and marsupialisation
Balloon Catheter insertion for treatment of Bartholin’s cyst or abscess under local anaesthetic
- Under local anaesthetic.
- Can be inserted on the day you come.
- You don’t need to fast before the procedure.
- You will be able to drive home/ take public transport after procedure. You may resume normal activities after 2-3 days (e.g exercise and sex).
- Success rate of 97%.
- Recurrence rate 4-17% (over 4 years).
- You may need follow up in 4 weeks.
Marsupialisation of Bartholin’s abscess or cyst
- Usually under general anaesthetic.
- You normally need to return at a later date for surgery.
- You need to fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure.
- You will need to be driven home due to general anaesthetic. You may resume normal activities after 2-3 weeks.
- Success rate of more than 90%.
- Recurrence rate up to 20% (over 4 years).
- You do not need to be followed up unless you have any concerns.
Surgical Excision of Bartholin’s gland
This is where the whole gland is removed. This procedure is considered a last resort and is sometimes offered if you have had several recurrences of a Bartholin’s cyst or abscess on the same side. Surgical excision will not be considered further in this leaflet, however, if you feel it may be relevant you may discuss it with the doctor caring for you.
What to expect after surgical management of Bartholin’s cyst/ abscess
It is common to feel the following symptoms
- Wound pain which can be controlled with pain medication as required.
- Wound oozing or slight bleeding which usually settles over the course of a week or two.
- If you have had a general anaesthetic you may experience nausea.
What are the risks of surgical management of Bartholin’s cysts or abscesses?
- Infection of the wound after the operation.
- Recurrence.
- Pain when passing urine – This normally resolves once the wound has healed.
- Pain during sexual intercourse – This normally resolves
- Once the wound is fully healed, rarely, long term pain may remain.
- Chronic discharge and fistula. Rarely, a persistent discharge from the area operated on may remain.
- General anaesthetic risks (if marsupialistion) – The risk of death from having a general anaesthetic (being put to sleep) is less than 1 in 200,000.
Informed Consent
This leaflet is provided to supplement verbal information that will be given to you by your healthcare provider prior to your procedure. Information sharing between you and the clinician is essential to ensure that your decision to consent is fully informed.
You have a right to be involved in these decisions and should feel supported to do so. Please take the time to consider what is important to you to ensure the information you receive is specific and individualised.